HI,使用研旭的开发板(使用内部基准),TI的例程(简单修改),将通道A0直接与模拟地相连,
然后进入Debug模式,得到的ADC转换平均值有时候为0左右,有时候为16左右,为什么偏差这么大???
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// ADC start parameters
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#define ADC_CKPS 0x1 // ADC module clock = HSPCLK/2*ADC_CKPS = 25.0MHz/(1*2) = 12.5MHz
//#define ADC_CKPS 0xA
#define ADC_SHCLK 0xf // S/H width in ADC module periods = 16 ADC clocks
#define AVG 1000 // Average sample limit
#define ZOFFSET 0x00 // Average Zero offset
#define BUF_SIZE 2048 // Sample buffer size
// Global variable for this example
Uint16 SampleTable[BUF_SIZE];
main()
{
Uint16 i;
Uint32 ulPlus = 0;
Uint32 ulAverage = 0;
Uint32 ulVoltage = 0;
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
// Specific clock setting for this example:
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.HISPCP.all = ADC_MODCLK; // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/ADC_MODCLK
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Specific ADC setup for this example:
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.ACQ_PS = ADC_SHCLK;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL3.bit.ADCCLKPS = ADC_CKPS;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.SEQ_CASC = 1; // 1 Cascaded mode
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.CONT_RUN = 1; // Setup continuous run
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Clear SampleTable
for (i=0; i<BUF_SIZE; i++)
{
SampleTable[i] = 0;
}
// Start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.all = 0x2000;
// Take ADC data and log the in SampleTable array
for(;;)
{
for (i=0; i<AVG; i++)
{
while (AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1== 0) {} // Wait for interrupt
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1;
SampleTable[i] =((AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0>>4) );
ulPlus += SampleTable[i];
}
ulAverage = ulPlus/AVG;
//ulVoltage = (ulAverage*3*1000)/4096;
ulVoltage = (ulPlus*3)/4096;
i = 0;
ulPlus = 0;
}
}
xiaopeng li:
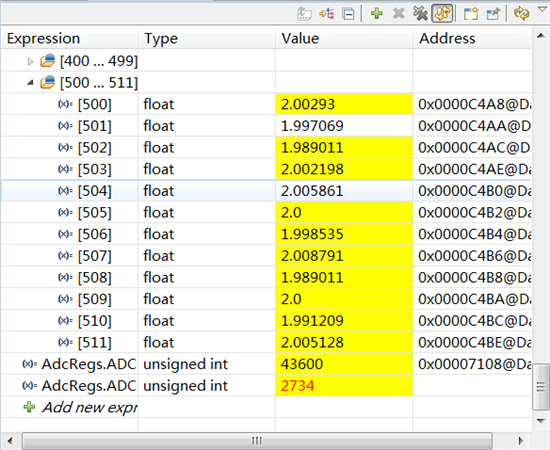
寄存器信息如下:
HI,使用研旭的开发板(使用内部基准),TI的例程(简单修改),将通道A0直接与模拟地相连,
然后进入Debug模式,得到的ADC转换平均值有时候为0左右,有时候为16左右,为什么偏差这么大???
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// ADC start parameters
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#define ADC_CKPS 0x1 // ADC module clock = HSPCLK/2*ADC_CKPS = 25.0MHz/(1*2) = 12.5MHz
//#define ADC_CKPS 0xA
#define ADC_SHCLK 0xf // S/H width in ADC module periods = 16 ADC clocks
#define AVG 1000 // Average sample limit
#define ZOFFSET 0x00 // Average Zero offset
#define BUF_SIZE 2048 // Sample buffer size
// Global variable for this example
Uint16 SampleTable[BUF_SIZE];
main()
{
Uint16 i;
Uint32 ulPlus = 0;
Uint32 ulAverage = 0;
Uint32 ulVoltage = 0;
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
// Specific clock setting for this example:
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.HISPCP.all = ADC_MODCLK; // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/ADC_MODCLK
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Specific ADC setup for this example:
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.ACQ_PS = ADC_SHCLK;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL3.bit.ADCCLKPS = ADC_CKPS;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.SEQ_CASC = 1; // 1 Cascaded mode
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.CONT_RUN = 1; // Setup continuous run
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Clear SampleTable
for (i=0; i<BUF_SIZE; i++)
{
SampleTable[i] = 0;
}
// Start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.all = 0x2000;
// Take ADC data and log the in SampleTable array
for(;;)
{
for (i=0; i<AVG; i++)
{
while (AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1== 0) {} // Wait for interrupt
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1;
SampleTable[i] =((AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0>>4) );
ulPlus += SampleTable[i];
}
ulAverage = ulPlus/AVG;
//ulVoltage = (ulAverage*3*1000)/4096;
ulVoltage = (ulPlus*3)/4096;
i = 0;
ulPlus = 0;
}
}
Forrest:
回复 xiaopeng li:
用例程试试,确保输入信号本身的精度,关于ADC精度下面的帖子可能能够帮到您:
http://bbs.eeworld.com.cn/thread-316019-1-1.html
HI,使用研旭的开发板(使用内部基准),TI的例程(简单修改),将通道A0直接与模拟地相连,
然后进入Debug模式,得到的ADC转换平均值有时候为0左右,有时候为16左右,为什么偏差这么大???
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// ADC start parameters
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#define ADC_CKPS 0x1 // ADC module clock = HSPCLK/2*ADC_CKPS = 25.0MHz/(1*2) = 12.5MHz
//#define ADC_CKPS 0xA
#define ADC_SHCLK 0xf // S/H width in ADC module periods = 16 ADC clocks
#define AVG 1000 // Average sample limit
#define ZOFFSET 0x00 // Average Zero offset
#define BUF_SIZE 2048 // Sample buffer size
// Global variable for this example
Uint16 SampleTable[BUF_SIZE];
main()
{
Uint16 i;
Uint32 ulPlus = 0;
Uint32 ulAverage = 0;
Uint32 ulVoltage = 0;
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
// Specific clock setting for this example:
EALLOW;
SysCtrlRegs.HISPCP.all = ADC_MODCLK; // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/ADC_MODCLK
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Specific ADC setup for this example:
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.ACQ_PS = ADC_SHCLK;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL3.bit.ADCCLKPS = ADC_CKPS;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.SEQ_CASC = 1; // 1 Cascaded mode
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.CONT_RUN = 1; // Setup continuous run
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Clear SampleTable
for (i=0; i<BUF_SIZE; i++)
{
SampleTable[i] = 0;
}
// Start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.all = 0x2000;
// Take ADC data and log the in SampleTable array
for(;;)
{
for (i=0; i<AVG; i++)
{
while (AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1== 0) {} // Wait for interrupt
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1;
SampleTable[i] =((AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0>>4) );
ulPlus += SampleTable[i];
}
ulAverage = ulPlus/AVG;
//ulVoltage = (ulAverage*3*1000)/4096;
ulVoltage = (ulPlus*3)/4096;
i = 0;
ulPlus = 0;
}
}
xiaopeng li:
回复 Forrest:
现在就是用的TI的例程adc_seqmode_test,通道A0直接连接模拟地,用万用表和示波器测量均为1mV,但debug模式下ADC得到的数据会为16mV左右。
 TI中文支持网
TI中文支持网