工程是直接使用的TI软件contr olSUITE中28335的例程adc_soc ,main函数具体如下
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
interrupt void adc_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example:
Uint16 LoopCount;
Uint16 ConversionCount;
Uint16 Voltage1[10];
Uint16 Voltage2[10];
main()
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
EALLOW;
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register
PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable ADCINT in PIE
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1;
IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
LoopCount = 0;
ConversionCount = 0;
// Configure ADC
AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x1; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS)
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl();
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start
// Wait for ADC interrupt
for(;;)
{
LoopCount++;
}
}
interrupt void adc_isr(void)
{
Voltage1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4;
Voltage2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4;
// If 40 conversions have been logged, start over
if(ConversionCount == 9)
{
ConversionCount = 0;
}
else ConversionCount++;
// Reinitialize for next ADC sequence
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE
return;
}
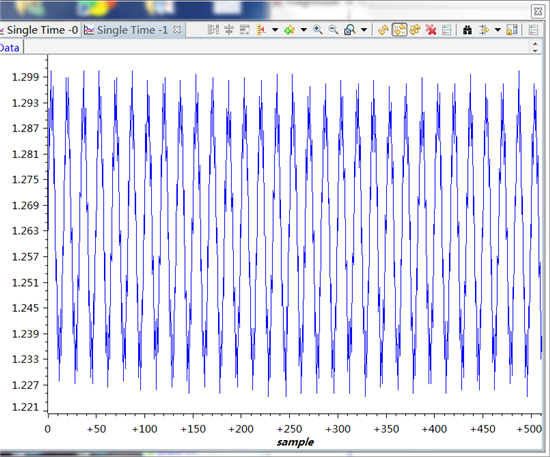
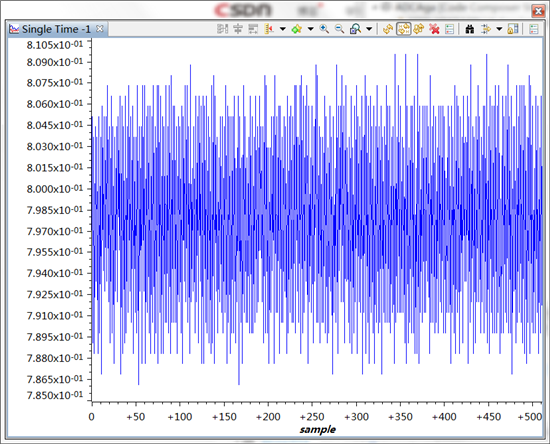
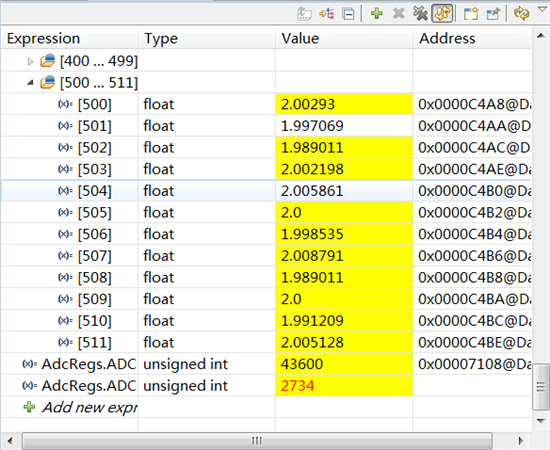
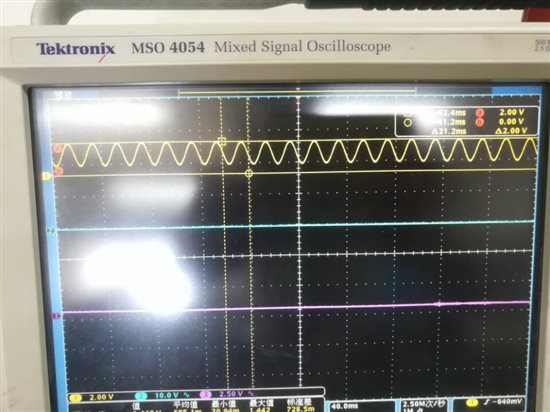
测试时在ADC 0脚接入了一节1.5V左右干电池,按道理AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 右移4位后数据应该在2000左右,但是通过CCS变量观察Voltage1数组成员值都在20一下,断点设置发现程序能顺利进入中断。在其他工程中使用CPU定时器程序启动ADC,测试结果正常也能说明ADC模块本身并没有问题。具体到EPWM方式启动,contr olSUITE中的几个例程运行结果都不正常。真心想知道是什么原因。对了,顺便问一下
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
在本工程中TBCLK是多少(没有看到CLKDIV和HSPCLKDIV设置啊)?还有如果按上面两行设置EPWM,那么正常由它驱动的ADC采样率具体是多少?麻烦给个具体数值,我按我的理解算一下,看是否一样。
囧:
对于TBCLK,如果没有设置就是默认,就是CLKDIV = 0,HSPCLKDIV = 1,TBCLK = SYSCLKOUT / (HSPCLKDIV × CLKDIV) 等于主时钟二分频。
ADC的SOC触发如代码所示:
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A groupEPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcountEPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event
PWM是向上计数模式,如下面代码所示:EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start
所以ADCSOC是在PWM1的向上计数模式,计数至COMPA的值时触发,采样的频率就是PWM的周期,假设采样最高输入时钟150MHZ,那EPWM的TBCLK就是75M,TBPRD为65535,那采样频率就是1/(75*1000000/65535)。
工程是直接使用的TI软件contr olSUITE中28335的例程adc_soc ,main函数具体如下
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
interrupt void adc_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example:
Uint16 LoopCount;
Uint16 ConversionCount;
Uint16 Voltage1[10];
Uint16 Voltage2[10];
main()
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
EALLOW;
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register
PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable ADCINT in PIE
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1;
IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
LoopCount = 0;
ConversionCount = 0;
// Configure ADC
AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x1; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS)
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl();
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start
// Wait for ADC interrupt
for(;;)
{
LoopCount++;
}
}
interrupt void adc_isr(void)
{
Voltage1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4;
Voltage2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4;
// If 40 conversions have been logged, start over
if(ConversionCount == 9)
{
ConversionCount = 0;
}
else ConversionCount++;
// Reinitialize for next ADC sequence
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE
return;
}
测试时在ADC 0脚接入了一节1.5V左右干电池,按道理AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 右移4位后数据应该在2000左右,但是通过CCS变量观察Voltage1数组成员值都在20一下,断点设置发现程序能顺利进入中断。在其他工程中使用CPU定时器程序启动ADC,测试结果正常也能说明ADC模块本身并没有问题。具体到EPWM方式启动,contr olSUITE中的几个例程运行结果都不正常。真心想知道是什么原因。对了,顺便问一下
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
在本工程中TBCLK是多少(没有看到CLKDIV和HSPCLKDIV设置啊)?还有如果按上面两行设置EPWM,那么正常由它驱动的ADC采样率具体是多少?麻烦给个具体数值,我按我的理解算一下,看是否一样。
Yang Liu19:
回复 囧:
嗯,感谢工程师回答,这些已经调通了。但是我发现在这个模式下,AD采样在500K左右就已经完全失真了。我想问,你们所说的上M采样,是直接用ACQ_PS,就是采样窗宽度,来平分AD时钟频率,然后设置AD连续采样?即采样频率= adc模块时钟/采样窗宽度 ,额我自己测试下没有成功,但是我想知道,这是否可行?
工程是直接使用的TI软件contr olSUITE中28335的例程adc_soc ,main函数具体如下
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
interrupt void adc_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example:
Uint16 LoopCount;
Uint16 ConversionCount;
Uint16 Voltage1[10];
Uint16 Voltage2[10];
main()
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
EALLOW;
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register
PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable ADCINT in PIE
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1;
IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
LoopCount = 0;
ConversionCount = 0;
// Configure ADC
AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x1; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS)
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl();
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start
// Wait for ADC interrupt
for(;;)
{
LoopCount++;
}
}
interrupt void adc_isr(void)
{
Voltage1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4;
Voltage2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4;
// If 40 conversions have been logged, start over
if(ConversionCount == 9)
{
ConversionCount = 0;
}
else ConversionCount++;
// Reinitialize for next ADC sequence
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE
return;
}
测试时在ADC 0脚接入了一节1.5V左右干电池,按道理AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 右移4位后数据应该在2000左右,但是通过CCS变量观察Voltage1数组成员值都在20一下,断点设置发现程序能顺利进入中断。在其他工程中使用CPU定时器程序启动ADC,测试结果正常也能说明ADC模块本身并没有问题。具体到EPWM方式启动,contr olSUITE中的几个例程运行结果都不正常。真心想知道是什么原因。对了,顺便问一下
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
在本工程中TBCLK是多少(没有看到CLKDIV和HSPCLKDIV设置啊)?还有如果按上面两行设置EPWM,那么正常由它驱动的ADC采样率具体是多少?麻烦给个具体数值,我按我的理解算一下,看是否一样。
囧:
回复 Yang Liu19:
如果连续采样一个通道,那也不可能达到只有采样窗的时间长度,转换还要80ns.
工程是直接使用的TI软件contr olSUITE中28335的例程adc_soc ,main函数具体如下
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
interrupt void adc_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example:
Uint16 LoopCount;
Uint16 ConversionCount;
Uint16 Voltage1[10];
Uint16 Voltage2[10];
main()
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
EALLOW;
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register
PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable ADCINT in PIE
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1;
IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
LoopCount = 0;
ConversionCount = 0;
// Configure ADC
AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x1; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS)
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl();
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start
// Wait for ADC interrupt
for(;;)
{
LoopCount++;
}
}
interrupt void adc_isr(void)
{
Voltage1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4;
Voltage2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4;
// If 40 conversions have been logged, start over
if(ConversionCount == 9)
{
ConversionCount = 0;
}
else ConversionCount++;
// Reinitialize for next ADC sequence
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE
return;
}
测试时在ADC 0脚接入了一节1.5V左右干电池,按道理AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 右移4位后数据应该在2000左右,但是通过CCS变量观察Voltage1数组成员值都在20一下,断点设置发现程序能顺利进入中断。在其他工程中使用CPU定时器程序启动ADC,测试结果正常也能说明ADC模块本身并没有问题。具体到EPWM方式启动,contr olSUITE中的几个例程运行结果都不正常。真心想知道是什么原因。对了,顺便问一下
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
在本工程中TBCLK是多少(没有看到CLKDIV和HSPCLKDIV设置啊)?还有如果按上面两行设置EPWM,那么正常由它驱动的ADC采样率具体是多少?麻烦给个具体数值,我按我的理解算一下,看是否一样。
libin li:
回复 Yang Liu19:
你好,我也碰到了这样的问题,你是如何调通的?
工程是直接使用的TI软件contr olSUITE中28335的例程adc_soc ,main函数具体如下
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
interrupt void adc_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example:
Uint16 LoopCount;
Uint16 ConversionCount;
Uint16 Voltage1[10];
Uint16 Voltage2[10];
main()
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
EALLOW;
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register
PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable ADCINT in PIE
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1;
IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
LoopCount = 0;
ConversionCount = 0;
// Configure ADC
AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x1; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS)
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl();
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start
// Wait for ADC interrupt
for(;;)
{
LoopCount++;
}
}
interrupt void adc_isr(void)
{
Voltage1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4;
Voltage2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4;
// If 40 conversions have been logged, start over
if(ConversionCount == 9)
{
ConversionCount = 0;
}
else ConversionCount++;
// Reinitialize for next ADC sequence
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE
return;
}
测试时在ADC 0脚接入了一节1.5V左右干电池,按道理AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 右移4位后数据应该在2000左右,但是通过CCS变量观察Voltage1数组成员值都在20一下,断点设置发现程序能顺利进入中断。在其他工程中使用CPU定时器程序启动ADC,测试结果正常也能说明ADC模块本身并没有问题。具体到EPWM方式启动,contr olSUITE中的几个例程运行结果都不正常。真心想知道是什么原因。对了,顺便问一下
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
在本工程中TBCLK是多少(没有看到CLKDIV和HSPCLKDIV设置啊)?还有如果按上面两行设置EPWM,那么正常由它驱动的ADC采样率具体是多少?麻烦给个具体数值,我按我的理解算一下,看是否一样。
RUI DAN1:
你好,我在调试adc_soc这个程序时也遇到了你那样的问题,测电源值很小,你是怎么解决的呢
工程是直接使用的TI软件contr olSUITE中28335的例程adc_soc ,main函数具体如下
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
interrupt void adc_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example:
Uint16 LoopCount;
Uint16 ConversionCount;
Uint16 Voltage1[10];
Uint16 Voltage2[10];
main()
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
EALLOW;
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register
PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable ADCINT in PIE
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1;
IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
LoopCount = 0;
ConversionCount = 0;
// Configure ADC
AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x1; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS)
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl();
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start
// Wait for ADC interrupt
for(;;)
{
LoopCount++;
}
}
interrupt void adc_isr(void)
{
Voltage1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4;
Voltage2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4;
// If 40 conversions have been logged, start over
if(ConversionCount == 9)
{
ConversionCount = 0;
}
else ConversionCount++;
// Reinitialize for next ADC sequence
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE
return;
}
测试时在ADC 0脚接入了一节1.5V左右干电池,按道理AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 右移4位后数据应该在2000左右,但是通过CCS变量观察Voltage1数组成员值都在20一下,断点设置发现程序能顺利进入中断。在其他工程中使用CPU定时器程序启动ADC,测试结果正常也能说明ADC模块本身并没有问题。具体到EPWM方式启动,contr olSUITE中的几个例程运行结果都不正常。真心想知道是什么原因。对了,顺便问一下
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
在本工程中TBCLK是多少(没有看到CLKDIV和HSPCLKDIV设置啊)?还有如果按上面两行设置EPWM,那么正常由它驱动的ADC采样率具体是多少?麻烦给个具体数值,我按我的理解算一下,看是否一样。
yong heng liao:
怎么解决得呢?
求解啊。。。。。
工程是直接使用的TI软件contr olSUITE中28335的例程adc_soc ,main函数具体如下
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
interrupt void adc_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example:
Uint16 LoopCount;
Uint16 ConversionCount;
Uint16 Voltage1[10];
Uint16 Voltage2[10];
main()
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
EALLOW;
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register
PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable ADCINT in PIE
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1;
IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
LoopCount = 0;
ConversionCount = 0;
// Configure ADC
AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x1; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS)
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl();
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start
// Wait for ADC interrupt
for(;;)
{
LoopCount++;
}
}
interrupt void adc_isr(void)
{
Voltage1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4;
Voltage2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4;
// If 40 conversions have been logged, start over
if(ConversionCount == 9)
{
ConversionCount = 0;
}
else ConversionCount++;
// Reinitialize for next ADC sequence
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE
return;
}
测试时在ADC 0脚接入了一节1.5V左右干电池,按道理AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 右移4位后数据应该在2000左右,但是通过CCS变量观察Voltage1数组成员值都在20一下,断点设置发现程序能顺利进入中断。在其他工程中使用CPU定时器程序启动ADC,测试结果正常也能说明ADC模块本身并没有问题。具体到EPWM方式启动,contr olSUITE中的几个例程运行结果都不正常。真心想知道是什么原因。对了,顺便问一下
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
在本工程中TBCLK是多少(没有看到CLKDIV和HSPCLKDIV设置啊)?还有如果按上面两行设置EPWM,那么正常由它驱动的ADC采样率具体是多少?麻烦给个具体数值,我按我的理解算一下,看是否一样。
Zhibin Yang:
回复 囧:
请问ADC采样频率最高能到多少,难道不是数据手册12.5M吗?我用连续采样一个通道测的采样频率为3.2M左右,是不是可以认为这就是最高采样频率?
工程是直接使用的TI软件contr olSUITE中28335的例程adc_soc ,main函数具体如下
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
interrupt void adc_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example:
Uint16 LoopCount;
Uint16 ConversionCount;
Uint16 Voltage1[10];
Uint16 Voltage2[10];
main()
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
EALLOW;
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register
PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable ADCINT in PIE
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1;
IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
LoopCount = 0;
ConversionCount = 0;
// Configure ADC
AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x1; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS)
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl();
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start
// Wait for ADC interrupt
for(;;)
{
LoopCount++;
}
}
interrupt void adc_isr(void)
{
Voltage1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4;
Voltage2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4;
// If 40 conversions have been logged, start over
if(ConversionCount == 9)
{
ConversionCount = 0;
}
else ConversionCount++;
// Reinitialize for next ADC sequence
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE
return;
}
测试时在ADC 0脚接入了一节1.5V左右干电池,按道理AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 右移4位后数据应该在2000左右,但是通过CCS变量观察Voltage1数组成员值都在20一下,断点设置发现程序能顺利进入中断。在其他工程中使用CPU定时器程序启动ADC,测试结果正常也能说明ADC模块本身并没有问题。具体到EPWM方式启动,contr olSUITE中的几个例程运行结果都不正常。真心想知道是什么原因。对了,顺便问一下
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
在本工程中TBCLK是多少(没有看到CLKDIV和HSPCLKDIV设置啊)?还有如果按上面两行设置EPWM,那么正常由它驱动的ADC采样率具体是多少?麻烦给个具体数值,我按我的理解算一下,看是否一样。
lei li10:
回复 Yang Liu19:
请问你是怎么调通的。感激不尽!
工程是直接使用的TI软件contr olSUITE中28335的例程adc_soc ,main函数具体如下
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
interrupt void adc_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example:
Uint16 LoopCount;
Uint16 ConversionCount;
Uint16 Voltage1[10];
Uint16 Voltage2[10];
main()
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
EALLOW;
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register
PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable ADCINT in PIE
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1;
IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
LoopCount = 0;
ConversionCount = 0;
// Configure ADC
AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x1; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS)
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl();
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start
// Wait for ADC interrupt
for(;;)
{
LoopCount++;
}
}
interrupt void adc_isr(void)
{
Voltage1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4;
Voltage2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4;
// If 40 conversions have been logged, start over
if(ConversionCount == 9)
{
ConversionCount = 0;
}
else ConversionCount++;
// Reinitialize for next ADC sequence
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE
return;
}
测试时在ADC 0脚接入了一节1.5V左右干电池,按道理AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 右移4位后数据应该在2000左右,但是通过CCS变量观察Voltage1数组成员值都在20一下,断点设置发现程序能顺利进入中断。在其他工程中使用CPU定时器程序启动ADC,测试结果正常也能说明ADC模块本身并没有问题。具体到EPWM方式启动,contr olSUITE中的几个例程运行结果都不正常。真心想知道是什么原因。对了,顺便问一下
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
在本工程中TBCLK是多少(没有看到CLKDIV和HSPCLKDIV设置啊)?还有如果按上面两行设置EPWM,那么正常由它驱动的ADC采样率具体是多少?麻烦给个具体数值,我按我的理解算一下,看是否一样。
Lei Yu5:
回复 Yang Liu19:
想问一下您怎么解决的?
工程是直接使用的TI软件contr olSUITE中28335的例程adc_soc ,main函数具体如下
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
interrupt void adc_isr(void);
// Global variables used in this example:
Uint16 LoopCount;
Uint16 ConversionCount;
Uint16 Voltage1[10];
Uint16 Voltage2[10];
main()
{
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
EALLOW;
#if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) // Default – 150 MHz SYSCLKOUT
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x3 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 150/(2*3) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
#if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ)
#define ADC_MODCLK 0x2 // HSPCLK = SYSCLKOUT/2*ADC_MODCLK2 = 100/(2*2) = 25.0 MHz
#endif
EDIS;
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected register
PieVectTable.ADCINT = &adc_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
InitAdc(); // For this example, init the ADC
// Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts:
// Enable ADCINT in PIE
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx6 = 1;
IER |= M_INT1; // Enable CPU Interrupt 1
EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM
ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM
LoopCount = 0;
ConversionCount = 0;
// Configure ADC
AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = 0x0001; // Setup 2 conv's on SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0x0; // Setup ADCINA3 as 1st SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 0x1; // Setup ADCINA2 as 2nd SEQ1 conv.
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.EPWM_SOCA_SEQ1 = 1;// Enable SOCA from ePWM to start SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1; // Enable SEQ1 interrupt (every EOS)
// Assumes ePWM1 clock is already enabled in InitSysCtrl();
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCAEN = 1; // Enable SOC on A group
EPwm1Regs.ETSEL.bit.SOCASEL = 4; // Select SOC from from CPMA on upcount
EPwm1Regs.ETPS.bit.SOCAPRD = 1; // Generate pulse on 1st event
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
EPwm1Regs.TBCTL.bit.CTRMODE = 0; // count up and start
// Wait for ADC interrupt
for(;;)
{
LoopCount++;
}
}
interrupt void adc_isr(void)
{
Voltage1[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 >>4;
Voltage2[ConversionCount] = AdcRegs.ADCRESULT1 >>4;
// If 40 conversions have been logged, start over
if(ConversionCount == 9)
{
ConversionCount = 0;
}
else ConversionCount++;
// Reinitialize for next ADC sequence
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.RST_SEQ1 = 1; // Reset SEQ1
AdcRegs.ADCST.bit.INT_SEQ1_CLR = 1; // Clear INT SEQ1 bit
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; // Acknowledge interrupt to PIE
return;
}
测试时在ADC 0脚接入了一节1.5V左右干电池,按道理AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0 右移4位后数据应该在2000左右,但是通过CCS变量观察Voltage1数组成员值都在20一下,断点设置发现程序能顺利进入中断。在其他工程中使用CPU定时器程序启动ADC,测试结果正常也能说明ADC模块本身并没有问题。具体到EPWM方式启动,contr olSUITE中的几个例程运行结果都不正常。真心想知道是什么原因。对了,顺便问一下
EPwm1Regs.CMPA.half.CMPA = 0x0080; // Set compare A value
EPwm1Regs.TBPRD = 0xFFFF; // Set period for ePWM1
在本工程中TBCLK是多少(没有看到CLKDIV和HSPCLKDIV设置啊)?还有如果按上面两行设置EPWM,那么正常由它驱动的ADC采样率具体是多少?麻烦给个具体数值,我按我的理解算一下,看是否一样。
user5352602:
回复 Lei Yu5:
回复一下问题答案,困扰了我2个小时,免得大家在困在同一个地方。我情况相同,采回来右移4位后值只有30几,多次检查后发现问题在ADCSOC初始化时没加上 EALLOW;SysCtrlRegs.HISPCP.all=ADC_MODCLK;//配置HSPCLK时钟为25MhzEDIS;
即没配置HISPCP 就会导致能进ADCSOC中断,但是采回来的值很小不对的情况。加上这句话在ADC初始化的最开始就行了
 TI中文支持网
TI中文支持网